Business Formation What are Some of the Advantages or Disadvantages of Forming a Corporation? :: Justia


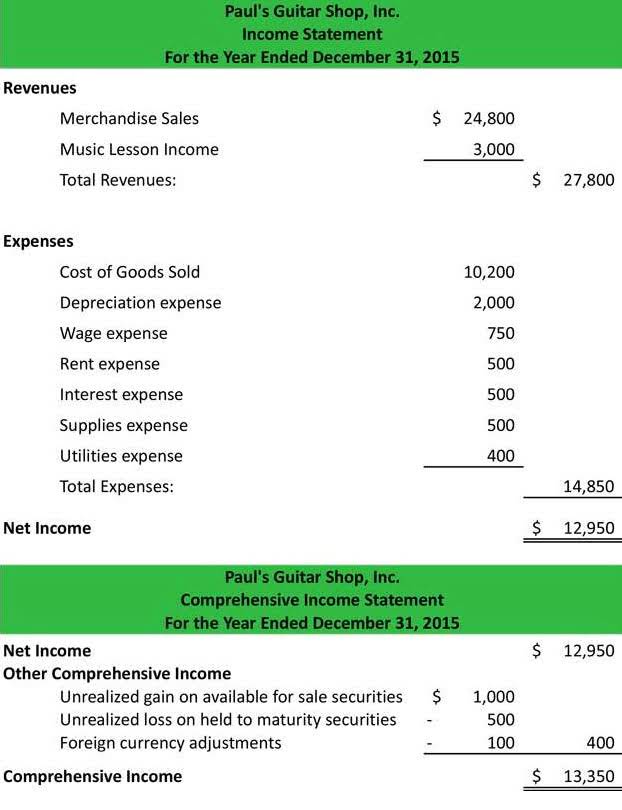
Perhaps you want to operate a small business S corp as opposed to a C corp, as the S corp can provide you with some additional benefits, particularly for tax purposes. The terms “C-corp” and “S-corp” refer to tax classifications that are available to both corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs). Corporations are taxed as C-corps by default, what are some advantages of a corporation but some corporations can elect S-corp taxation instead. LLCs are typically taxed as sole proprietorships or partnerships, but they can also choose to be taxed as C-corps or S-corps. The profits of a C corporation are effectively taxed twice, first when the company files its income taxes, and again when those profits are distributed as dividends.
Where Should We Send The Downloadable File?
Owners can decide to quit a corporation, but that doesn’t mean the company is going to dissolve immediately. A sole proprietor can decide instantly to stop working and that immediately closes everything. When the agency is a B, C, or S-corporation, then a resolution to dissolve must come through the leadership structure. This document must go to the jurisdiction that governs the region to indicate that no business activities will occur in the future. Tax returns must be filed for that period while regulatory compliance continues.

Double taxation
Creating a limited liability company (LLC) is a much simpler process than creating a corporation and generally takes less paperwork. LLCs are under the jurisdiction of state law, so the process of forming an LLC depends on the state where it is being filed. Are you the owner of a business who is unsure about whether it is appropriate to incorporate your activities? Then the best outcome from this guide to the pros and cons of corporations is to speak with a legal professional familiar with this area of the law.


Incorporation: Definition, How It Works, and Advantages


Instead, shareholders pay taxes on the dividends they receive from the corporation on their personal income tax returns. Corporations differ from sole proprietorships, partnerships and LLCs in a number of ways. A corporation is a company or group acting as a single entity and has shareholders, directors and officers working in association. Corporations are subject to a number of legal and/or tax requirements other types of businesses are not.
How do I form a corporation?
- If the owners agree to pursue that structure for obtaining capital, then there is still personal liability within the company.
- For example, the owner of a sole proprietorship can easily convert it into a partnership or a corporation.
- This policy ensures that S Corps do not end up with unqualified shareholders that might lead to the termination of the S Corp status.
- One of the problems of corporations is that their management is separate from their shareholders.
- It requires a great deal more paperwork, meeting many more guidelines, electing a board of directors, adopting bylaws, having annual meetings, and creating formal financial statements.
Incorporating your company can cost a great deal of money depending on the state where you plan for your business to operate. If you need help with the required incorporation paperwork, you may want to hire an attorney. While hiring an attorney is not a requirement for incorporation, having an experienced legal professional on your side can make the process much easier. Nonprofit corporations are formed for reasons other than shareholder profit. These people are eligible for important tax breaks at state and federal levels, including exemption from federal income tax.
Pros of Forming a Corporation
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) does not view an LLC as a separate vehicle for tax purposes, which allows for greater flexibility. They can be treated as a sole proprietorship, a partnership, or a corporation. The most common tax option of an LLC is taxation similar to a sole proprietorship.
Should the registered agent move out of the state in which the business is incorporated in, the company will need to choose a new agent. There are also online legal services that can act as your registered agent (in return for a fee). As a rule, the shareholders are only responsible for the payment of their own shares. As owners, the shareholders are entitled to receive the profits of the company, usually in the form of dividends. The board of directors comprises a group of individuals who are elected to represent shareholders. They are tasked with making decisions on major issues affecting the shareholders, and they also create policies to guide the management and daily operations of the corporation.
The life of a corporate entity lasts until there is a change in its charter or the purpose of its existence has reached its peak. A process called liquidation will serve the transition, facilitated by a liquidator. Not-for-profit entities operate under the category of charitable organizations, which are dedicated to a particular social cause such as educational, religious, scientific, or research purposes. Rather than distribute revenues to shareholders, not-for-profit organizations use their revenues to further their objectives. As with any business structure, each of these has its pros and cons. To decide which works for you, analyze your business needs and the nature of your business carefully.
- Post your legal need if you need help choosing which business entity is best for you or whether to form an S Corp or a C Corp.
- Its shareholders will only be liable for the corporation’s debts limited to the value of their shareholding or their capital invested in the corporation.
- Rather than distribute revenues to shareholders, not-for-profit organizations use their revenues to further their objectives.
- As an individual starting their own business, it’s important to understand all of the nuances involved and choose the right structure for your company.
- A member has to pay taxes themselves on the profits of the LLC as opposed to the LLC paying the taxes.
- Treasury proposed S-corp status as a solution that could give smaller American businesses a leg up in an increasingly conglomerated corporate landscape.
How do I form a C-corp?